Déployer une Application Next.js avec Terraform
Ce projet m’a permis de déployer un site web statique en utilisant du stockage objet et un CDN pour la toute première fois — une expérience concrète super enrichissante. C’était particulièrement motivant de bosser sur un cas proche des conditions réelles. Ce projet faisait partie du programme de la Cloud Engineer Academy, ce qui m’a encore plus aidé à approfondir mes connaissances des technos cloud.
1 — Besoins
2 — S3 & CloudFront
3 — Déploiement
4 — Conclusion
1 - Besoins
Contexte du Scénario
Client : James Smith, développeur web freelance
Projet : Mise en ligne de son portfolio
Description : James a conçu une landing page moderne en Next.js pour mettre en avant ses projets. Il cherche une solution fiable, scalable et économique pour l’héberger. Le site doit être rapide à charger partout dans le monde et rester disponible à tout moment.
Mon rôle : En tant qu’équipe DevOps, notre mission est de déployer ce site en utilisant AWS, via Terraform. Une vraie mise en situation concrète : S3 pour l’hébergement statique, CloudFront pour la distribution mondiale, et Terraform pour l’automatisation.
Problématique
Le site doit être :
- Hautement disponible : accessible partout, tout le temps.
- Scalable : capable de gérer plus de trafic si besoin.
- Économique : pas de coûts inutiles.
- Rapide : bonne expérience utilisateur.
Solution idéale : hébergement statique sur S3 + distribution via CloudFront, le tout automatisé avec Terraform.
Objectifs du Projet
À la fin du projet, on aura :
- Déployé un site Next.js sur AWS
- Automatisé l’infrastructure avec Terraform
- Distribué le contenu mondialement avec CloudFront
- Appliqué des bonnes pratiques de sécurité et de performance
- Mis en ligne le code sur GitHub
Voici l’architecture :

On utilise ici le template Next.js de base pour simplifier, mais on pourrait l’adapter à n’importe quel site statique.
2 - S3 & CloudFront
L’utilisation combinée de CloudFront et S3 permet de créer un CDN rapide, sécurisé et scalable. CloudFront délivre le contenu depuis des serveurs proches de l’utilisateur → moins de latence.
Je n’avais jamais utilisé de CDN avant, donc j’ai pris le temps de lire la doc : finalement, c’est assez simple !
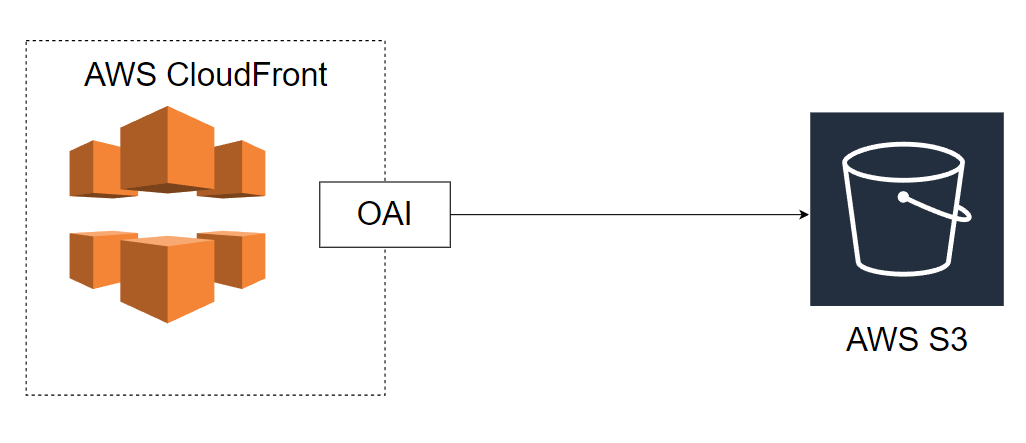
Le schéma ci-dessus montre les communications et relations entre le bucker S3 et CloudFront, and OAI. Voici comment ces composants travaille ensemble :
- CloudFront :
- Point d’entrée public.
- Configure comme origine notre bucket S3 pour servir le contenu static (
index.html…).
- S3 Bucket :
- Contient les fichiers du site (HTML, JS, CSS…).
- Doit rester privé.
- OAI (Origin Access Identity) :
- Une Identité qui permet à CloudFront d’accéder au bucket S3 de façon sécurisée.
- Cela assure que seulement CloudFront puisse accèder au bucket S3.
- Bucket Policy :
- Autorise uniquement CloudFront (via l’OAI) à lire le contenu.
3. Deployement
Le projet entier est accessible ici.
Étape 1 : accès public (non recommandé)
J’avais commencé par autorisé un accès publique par n’importe qui de n’importe où pour ensuite affiner.
provider "aws" {
region = "eu-west-3"
}
# Create a new S3 bucket
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "portfolio_is_bucket" {
bucket = "portfolio-nextjs-is"
tags = {
Name = "portfolio-nextjs-is"
}
}
# Enable bucket ownership controls to enforce bucket owner permissions
resource "aws_s3_bucket_ownership_controls" "portfolio_is_ownership_controls" {
depends_on = [
aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket
]
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket.id
rule {
object_ownership = "BucketOwnerPreferred"
}
}
# Disable public access block to allow public access to the bucket
resource "aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block" "portfolio_is_public_access_block" {
depends_on = [
aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket
]
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket.id
# Set everything to false to allow public access to the bucket
block_public_acls = false # Block public ACLs
block_public_policy = false # Block public bucket policies
ignore_public_acls = false # Ignore public ACLs
restrict_public_buckets = false # Block public and cross-account access to buckets
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_policy" "portfolio-bucket_policy" {
depends_on = [
aws_s3_bucket.portfolio-bucket,
aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block.my_bucket_public_access_block
]
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.portfolio-bucket.id
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17",
Statement = [
{
Sid = "PublicReadGetObject",
Effect = "Allow",
Principal = "*",
Action = "s3:GetObject",
Resource = "${aws_s3_bucket.portfolio-bucket.arn}/*",
},
],
})
# Enable the bucket to host a static website
resource "aws_s3_bucket_website_configuration" "portfolio_is_website" {
depends_on = [
aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket
]
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket.id
index_document {
suffix = "index.html"
}
error_document {
key = "index.html"
}
}
# Create an origin access identity to allow CloudFront to reach the bucket
resource "aws_cloudfront_origin_access_identity" "portfolio_is_origin_access_identity" {
comment = "Allow CloudFront to reach the bucket"
}
# Create a CloudFront distribution to serve the static website
resource "aws_cloudfront_distribution" "portfolio_is_cloudfront" {
# Describes the origin of the files that you want CloudFront to distribute
origin {
domain_name = aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket.bucket_regional_domain_name
origin_id = aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket.id # unique identifier for the origin
s3_origin_config {
origin_access_identity = aws_cloudfront_origin_access_identity.portfolio_is_origin_access_identity.cloudfront_access_identity_path
}
}
enabled = true # enable cloud front distribution directly after creation
is_ipv6_enabled = true # enable IPv6 support
default_root_object = "index.html" # default root object to serve when a request is made to the root domain
default_cache_behavior {
allowed_methods = ["GET", "HEAD", "OPTIONS"] # HTTP methods that CloudFront processes and forwards to the origin
cached_methods = ["GET", "HEAD"] # HTTP methods for which CloudFront caches responses
target_origin_id = aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket.id
# Forward the query string to the origin that is associated with this cache behavior
forwarded_values {
query_string = false
cookies {
forward = "none"
}
}
viewer_protocol_policy = "redirect-to-https" # HTTP and HTTPS requests are automatically redirected to HTTPS
min_ttl = 0 # minimum amount of time that you want objects to stay in a CloudFront cache
default_ttl = 3600 # default amount of time (in seconds) that you want objects to stay in CloudFront caches
max_ttl = 86400 # maximum amount of time (in seconds) that you want objects to stay in CloudFront caches
}
# Allow cloudfront to use default certificate for ssl
viewer_certificate {
cloudfront_default_certificate = true
}
# Define restrictions on the geographic distribution of your content
restrictions {
geo_restriction {
restriction_type = "none"
}
}
tags = {
Name = "portfolio-cloudfront-nextjs-is"
}
}Étape 2 : restriction d’accès via CloudFront uniquement
Ensuite, on sécurise : le bucket S3 devient privé, et on configure l’accès via OAI.
On veut donc seulement que l’accès à nos fichiers stockés sur le bucket S3 soient accessible via CloudFront.
Avant, j’avais laissé le bucket accessible publiquement → pas top niveau sécurité. Là, on restreint bien l’accès via OAI. Il faut aussi créer une bucket policy pour pour autoriser l’accès au bucket.
Le fichier de policy Terraform autorise seulement CloudFront à accéder aux fichiers.
provider "aws" {
region = "eu-west-3"
}
# Create a new S3 bucket
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "portfolio_is_bucket" {
bucket = "portfolio-nextjs-is"
tags = {
Name = "portfolio-nextjs-is"
}
}
# Enable bucket ownership controls to enforce bucket owner permissions
resource "aws_s3_bucket_ownership_controls" "portfolio_is_ownership_controls" {
depends_on = [
aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket
]
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket.id
rule {
object_ownership = "BucketOwnerPreferred"
}
}
# Disable public access block to allow public access to the bucket
resource "aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block" "portfolio_is_public_access_block" {
depends_on = [
aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket
]
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket.id
# Set everything to false to allow public access to the bucket
block_public_acls = true # Block public ACLs
block_public_policy = true # Block public bucket policies
ignore_public_acls = true # Ignore public ACLs
restrict_public_buckets = true # Block public and cross-account access to buckets
}
################################
# ACLs are used to have more fine-grained control over objects in the bucket | Not needed for now
# # Set the bucket Access Control List to public-read allowing public read access to the bucket
# resource "aws_s3_bucket_acl" "bucket_acl" {
# depends_on = [
# aws_s3_bucket_ownership_controls.bucket_ownership_controls,
# aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block.my_bucket_public_access_block
# ]
# bucket = aws_s3_bucket.portfolio-bucket.id
# acl = "public-read"
# }
################################
# Create a bucket policy to allow read access only from CloudFront
resource "aws_s3_bucket_policy" "portfolio_is_bucket_policy" {
depends_on = [
aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket,
aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block.my_bucket_public_access_block,
aws_cloudfront_origin_access_identity.origin_access_identity
]
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket.id
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17",
Statement = [
{
Sid = "PublicReadGetObject",
Effect = "Allow",
Principal = {
AWS = "${aws_cloudfront_origin_access_identity.origin_access_identity.iam_arn}" # The ARN of the CloudFront origin access identity
},
Action = "s3:GetObject",
Resource = "${aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket.arn}/*",
},
],
})
}
################################
# Allow public read access to the bucket from any IP address | We do not want that
# resource "aws_s3_bucket_policy" "portfolio-bucket_policy" {
# depends_on = [
# aws_s3_bucket.portfolio-bucket,
# aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block.my_bucket_public_access_block
# ]
# bucket = aws_s3_bucket.portfolio-bucket.id
# policy = jsonencode({
# Version = "2012-10-17",
# Statement = [
# {
# Sid = "PublicReadGetObject",
# Effect = "Allow",
# Principal = "*",
# Action = "s3:GetObject",
# Resource = "${aws_s3_bucket.portfolio-bucket.arn}/*",
# },
# ],
# })
# }
################################
# Enable the bucket to host a static website
resource "aws_s3_bucket_website_configuration" "portfolio_is_website" {
depends_on = [
aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket
]
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket.id
index_document {
suffix = "index.html"
}
error_document {
key = "index.html"
}
}
# Create an origin access identity to allow CloudFront to reach the bucket
resource "aws_cloudfront_origin_access_identity" "portfolio_is_origin_access_identity" {
comment = "Allow CloudFront to reach the bucket"
}
# Create a CloudFront distribution to serve the static website
resource "aws_cloudfront_distribution" "portfolio_is_cloudfront" {
# Describes the origin of the files that you want CloudFront to distribute
origin {
domain_name = aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket.bucket_regional_domain_name
origin_id = aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket.id # unique identifier for the origin
s3_origin_config {
origin_access_identity = aws_cloudfront_origin_access_identity.portfolio_is_origin_access_identity.cloudfront_access_identity_path
}
}
enabled = true # enable cloud front distribution directly after creation
is_ipv6_enabled = true # enable IPv6 support
default_root_object = "index.html" # default root object to serve when a request is made to the root domain
default_cache_behavior {
allowed_methods = ["GET", "HEAD", "OPTIONS"] # HTTP methods that CloudFront processes and forwards to the origin
cached_methods = ["GET", "HEAD"] # HTTP methods for which CloudFront caches responses
target_origin_id = aws_s3_bucket.portfolio_is_bucket.id
# Forward the query string to the origin that is associated with this cache behavior
forwarded_values {
query_string = false
cookies {
forward = "none"
}
}
viewer_protocol_policy = "redirect-to-https" # HTTP and HTTPS requests are automatically redirected to HTTPS
min_ttl = 0 # minimum amount of time that you want objects to stay in a CloudFront cache
default_ttl = 3600 # default amount of time (in seconds) that you want objects to stay in CloudFront caches
max_ttl = 86400 # maximum amount of time (in seconds) that you want objects to stay in CloudFront caches
}
# Allow cloudfront to use default certificate for ssl
viewer_certificate {
cloudfront_default_certificate = true
}
# Define restrictions on the geographic distribution of your content
restrictions {
geo_restriction {
restriction_type = "none"
}
}
tags = {
Name = "portfolio-cloudfront-nextjs-is"
}
}Étape 3 : build + upload du site
Il faut appliquer le configuration avec Terraform. CloudFront prends un peu de temps pour etre up. Ensuite il suffit de builder notre application next-js :
npm run buildPuis on copie les fichiers du dossier out/ dans le bucket S3.
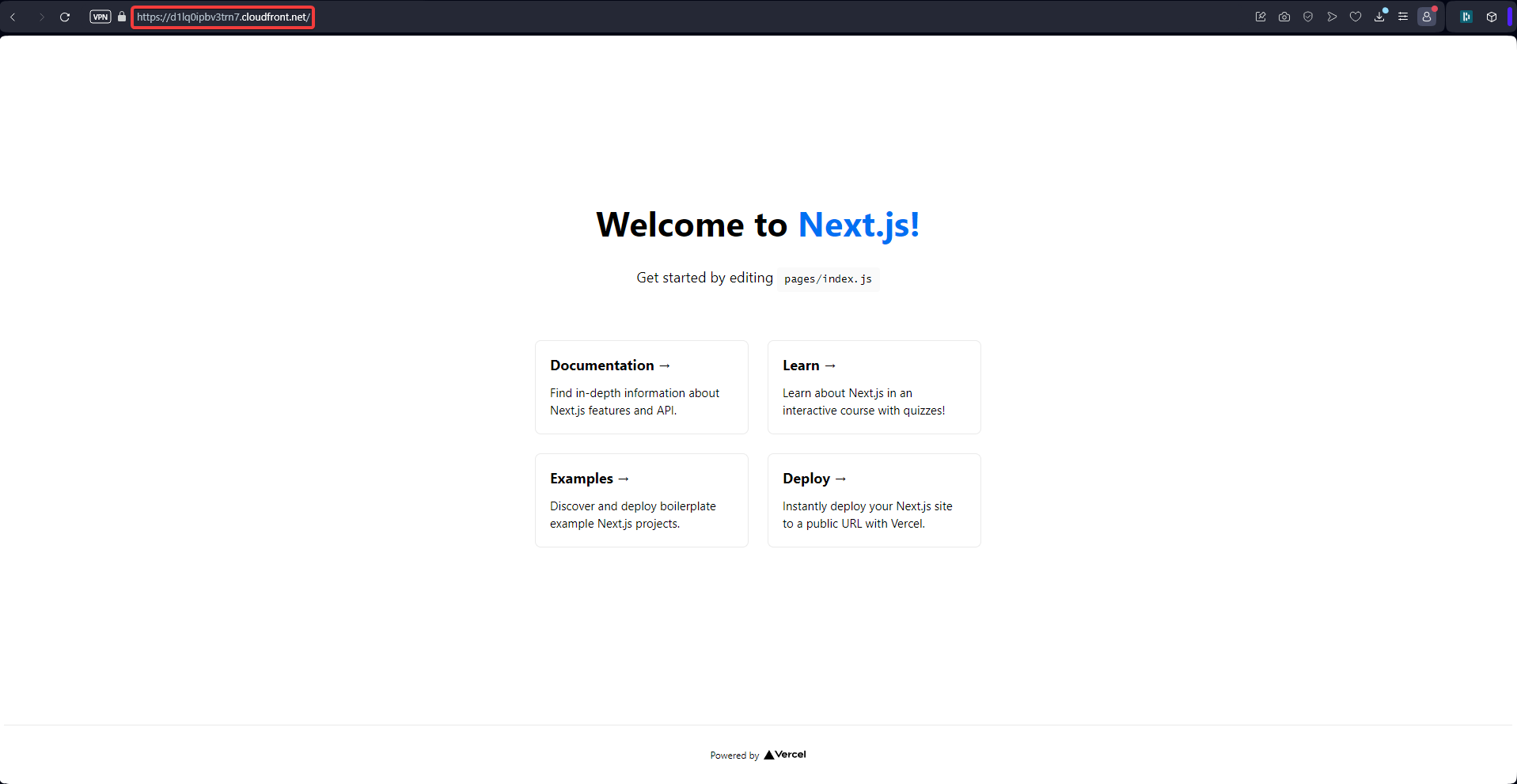
Le site est bien servi par CloudFront uniquement (testé dans le navigateur)
Conclusion | Best practices
Quelques bonnes pratiques observées :
- Toujours mettre les noms de ressources entre guillemets
- Utiliser des underscores au lieu de tirets (portfolio_nextjs_is)
- Ne jamais mettre le type dans le nom (aws_s3_bucket.portfolio)
Si on fait un terraform destroy, il faut vider le bucket S3 avant, sinon la suppression échoue.