
Enhancing my Cloud Skills - Week 4 - Linux & Bash
Linux is a powerful open-source operating system widely used for server environments, development, and cloud computing. Bash (Bourne Again SHell) is a Unix shell and command language that provides a command-line interface to interact with the Linux operating system.
1 — Linux File System
2 — Linux Basic Commands
3 — Creating an EC2 Instance in AWS #new
4 — Linux File Permissions
1 - Linux File System
The Linux file system is organized in a hierarchical directory structure. Each directory has a specific purpose:
- /: The root directory. The top-level directory in the Linux file system, containing all other directories and files.
- /home: Contains personal directories for each user. Users’ personal files and directories are stored here (e.g.,
/home/user1). - /etc: Stores system configuration files. These files are read by the system and applications at startup to configure the environment and software.
- /var: Contains files that continuously change, such as logs, caches, and spool files. It’s commonly used for data that grows over time, like system logs (
/var/log). - /bin: Stores executable binaries and system programs available to all users. Common commands like
ls,cat, andcpare located here. - /lib: Holds shared libraries needed by programs in
/binand/sbin. These libraries are essential for the basic functioning of the system. - /tmp: A temporary storage location where any user can create files. Data in
/tmpis usually cleared on system reboot. - /usr: Contains user system resources. Includes:
- /usr/bin: Binaries installed by the user, such as applications not critical for system boot, like
git. - /usr/local: Software and binaries installed manually by the system administrator.
- /usr/bin: Binaries installed by the user, such as applications not critical for system boot, like
- /sbin: Contains system binaries for system administration tasks, typically only used by the root user. Examples include
fdiskandifconfig. - /root: The home directory for the root user (system administrator). It is separate from
/hometo ensure the root user has access even if/homeis not mounted. - /run: A runtime directory containing data describing the system’s state since the last boot. It includes information about user sessions, logging daemons, and
systemddetails. - /proc: A virtual filesystem that provides information about system processes and hardware. It includes files like
/proc/cpuinfofor CPU information and/proc/mountsfor mounted filesystems. - /sys: Another virtual filesystem that exposes information about the kernel and hardware devices (e.g., mice, keyboards). It’s used to interact with and configure system hardware.
2 - Linux Basic Commands
In Linux, Bash is used to interact with the operating system. Bash acts as an interface between the user and the Linux environment, interpreting and executing commands.
Common Bash Commands:
ls # Lists files in the current directory
ls -a # Lists all files, including hidden ones
ls -l # Lists files with detailed information (permissions, size, date, etc.)
cd [directory] # Changes the current directory
pwd # Prints the current working directory
cat [filename] # Displays the content of a file
touch [filename] # Creates a new empty file
nano [filename] # Opens the Nano text editor with the specified file
mkdir [directory] # Creates a new directory
Using Vim (Text Editor):
Vim is a powerful text editor in Linux. Here are some basic commands to use Vim:
# Open Vim with a file
vim [filename]- i => Enter insert mode to start editing the file.
- Esc =>Return to normal mode.
- :w => Save changes to the file.
- :q => Quit Vim.
- :wq => Save changes and quit Vim.
3 - Creating an EC2 Instance in AWS #new
Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) allows you to create virtual servers in the AWS cloud.
Steps to Create an EC2 Instance:
- Go to the EC2 dashboard in the AWS Management Console.
- Select Amazon Linux as the operating system for the instance.
- Create and launch the instance.
Amazon Linux comes with the AWS CLI pre-installed and pre-configured, making it quicker to use than other cloud providers like Azure, where you need to manually install and configure the CLI.
Accessing AWS Services from EC2:
- By attaching appropriate roles to the EC2 instance, you can directly interact with AWS services (e.g., copying files to an S3 bucket) without needing to manually configure credentials.
4 - Linux File Permissions
Linux uses a permission system to control access to files and directories. Each file and directory has permissions for three types of users: owner, group, and others.
Understanding File Permissions:
The output of the ls -l command provides detailed file information, including permissions:
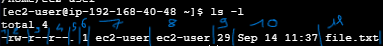
-rw-r--r-- 1 owner group size date filename- Indicate if its a file (-) or a directory (d)
- The owner of the file have r (read) and w (write) permissions but doesn’t have x (execute) permission.
- The group have only r (read) permission.
- Other users have also r (read) permission.
- Links (directory have 2, 1 for themselves and 1 for the parent directory)
- Owner
- Group
- Size of the file in byte
- Last opened date
Permissions in Directories:
r(read): Allows listing files in the directory.w(write): Allows creating, deleting, and renaming files within the directory.x(execute): Allows accessing the directory, including reading file data and changing into it.
Modifying Permissions:
The chmod command changes file or directory permissions:
chmod +x file # Add execute permission
chmod -r file # Remove read permission
chmod 755 file # Set permissions using numerical mode (rwxr-xr-x)Numerical Permission Representation:
4: Read (r)2: Write (w)1: Execute (x)
Example: chmod 755 file sets:
- Owner:
7(read, write, execute) - Group:
5(read, execute) - Others:
5(read, execute)
5 - Conclusion
I already known all theses concepts it was just a good reminding of everything.